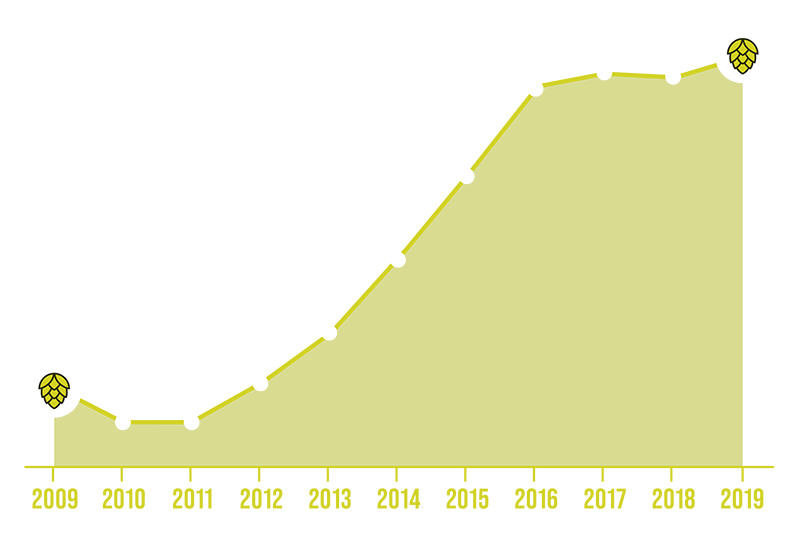
hop aromas
Inside a hop
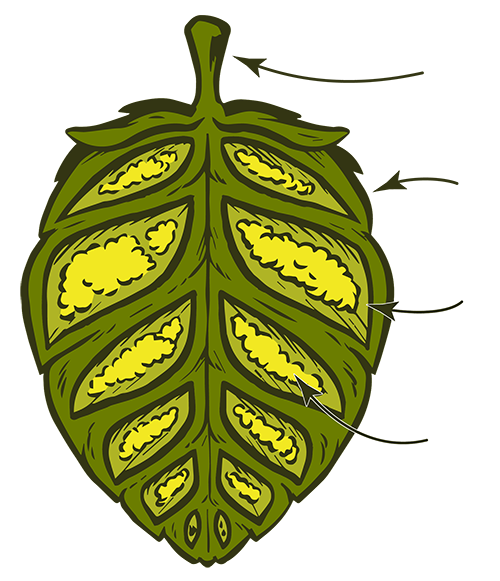

Where do hop flavors and aromas come from?

A dried hop cone contains...




Getting
the most
out of your
Hop oil
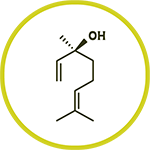
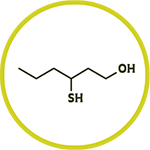
Some oils from the oxygenated fraction are odorless because they are bound to other molecules.
Releasing these molecules can boost the aroma.
——— But how? ———
BOOSTING AROMAS withHOP BIOTRANSFORMATION

Hops contain aroma compounds that are bound to non-volatile conjugates.
Yeast-derived enzymes can cleave the conjugate to release these compounds and boost hop flavor and aroma.
Yeast facilitates Hop Biotransformation and optimizes flavor and aroma from less aromatic hop varieties.
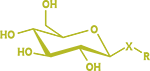
What are hop glycosides?
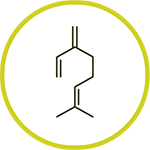
A glycoside is a compound that is chemically bound to a sugar molecule. In hops, aroma compounds such as terpenes are bound to sugars as glycosides in the green matter of the hop. Terpene glycosides play a role in hop biotransformation.
Yeast’s role in beer aroma
Yeast also naturally produces β-glucosidase enzymes, turning non-aromatic glycosides into aromatic terpenes.
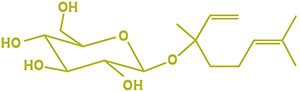




β-GLUCOSIDASE ACTIVITY DIFFERS BY YEAST STRAIN


Can exogenous β-glucosidase enzymes boost biotransformation?
Lallemand conducted global trials using an enzyme formulation based on β-glucosidase and compared the results to a control beer.






-
Increases the diversity of hop flavors and aroma by changing the ratio of specific terperne compounds
-
Enhances the beer mouthfeel and drinkability by reducing unpleasant, harsh bitterness
-
Increases wort fermentability
-
Increases beer aroma complexity when combined with selected yeasts
-
Enhances hop flavor and aroma
 from less
from less 
Almaguer, C., Schönberger, C., Gastl, M., Arendt, E. K., & Becker, T. (2014). Humulus lupulus - A story that begs to be told. A review. J. Inst. Brew., 120(4), 289-314.
Barth-Haas (2019). Hop market update Barth-Haas Group (Last update Nov. 27th 2019).
Lallemand (2020). Best Practices: Biotransformation. Retrieved from www.lallemandbrewing.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/LAL-bestpractices-Biotransformation2020.pdf

